
We’ll learn the steps of converting Wire Gauge(AWG) to wire cross-section area in units of inches 2, mm 2, and kilo-circular mils (kcmil) in this section.
#WIRE AMPACITY CHART INSTALL#
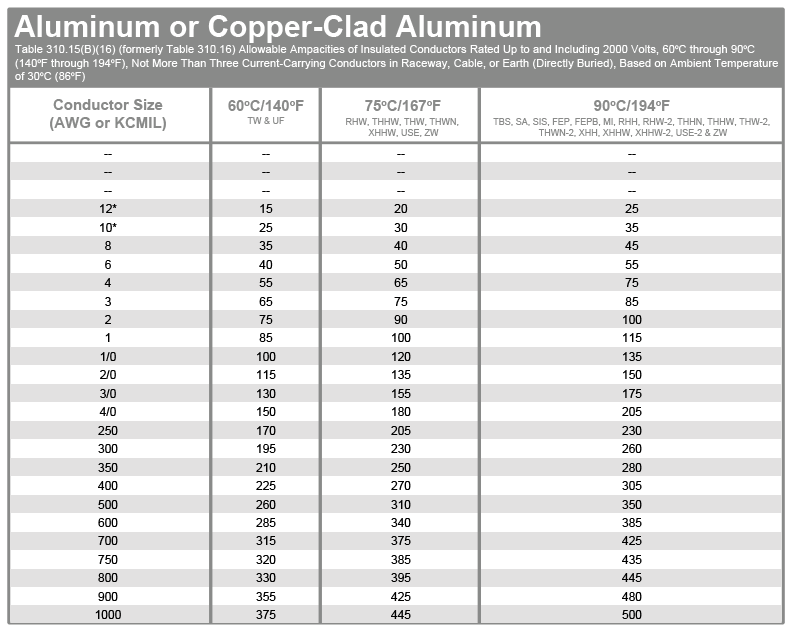
Chapter 2: Calculating Wire Size (Diameter & Area) from Wire Gaugeīefore you decide which wire to install on your residential or commercial electric circuits/system, it’s very important to learn the parameters of the wire. Hence, the change of temperature is one of the contributing factors in ampacity. If you change the temperature from 60 0C to 90 0C of the first wire(8 AWG copper), the ampacity would increase to 40 amp. Let’s clarify this with a couple of examples:Ī copper wire of 8 AWG will have a 30 amp load-bearing capacity at 60 0C, where another wire of 2 AWG will have 95 amp capacity under the same temperature. When it comes to determining the load-bearing capacity or the ampacity of a wire, a change in any of these factors would change the ampacity of the wire. The unit of ampacity is ‘Ampere’.Īmpacity varies on what gauge of wire, the metal of the wire you’re talking about, what temperature the wire is at, and a few other environmental factors. In other words, you can also call it a wire’s load-bearing capability. It simply defines the maximum ability to carry electricity of a wire under normal conditions. What is Ampacity/Load Bearing Capacity?Īmpacity is the short form of ‘Ampere Capacity’ and had been sourced from the word ‘Ampere or Amp’.
#WIRE AMPACITY CHART HOW TO#
Throughout the guide, we’d rather stick to mostly AWG, and show you how to convert from AWG to mm/mm 2 and in/in 2. Millimeter(mm) and millimeter-square(mm 2)Īs per convenience, MCM or kcmil are pretty backdated metrics of wire gauge.MCM(Multi-Chip Module) or kcmil(1 thousand circular mils).But for now, let’s have a look at all of the convenient wire gauge metrics across the globe: We’ll talk about this standard later in this guide. Here, AWG is one of the convenient standards to measure and express wire gauge. Where a smaller 2 AWG wire is 6.54mm in diameter and 33.6mm 2 in terms of area. You’ll see the following AWG gauges in the market: Smaller wire gauge numbers mean thinner wires, and higher gauge numbers mean thicker wires.Īcross the globe, the most accepted wire gauge metric is AWG or American Wire Gauge. It’s usually represented by a number, and there are no particular units of it. Simply put, a wire gauge is a metric to signify the thickness and area of round and solid electric wires. Final Words Chapter 1: Definitions What is Wire Gauge?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
